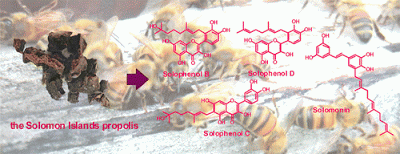
Solophenols B–D and Solomonin: New Prenylated Polyphenols
Isolated from Propolis Collected from The Solomon Islands and Their
Antibacterial Activity
J. Agric. Food Chem, Publication Date (Web): October 15,
2012
Three new prenylated flavonoids, namely, solophenols B (1),
C (2), and D (3), as well as a new prenylated stilbene, solomonin (4), were
isolated from propolis collected from the Solomon Islands. In addition, 17
known compounds were identified. The structures of the new compounds were
determined by a combination of methods, including mass spectrometry and NMR.
These new compounds and several known compounds were tested for antibacterial
activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, and Pseudomonas
aeruginosa. Most of them exhibited potent antibacterial activity. These
findings may indicate that propolis from the Solomon Islands has potential
applications as an ingredient in food additives or pharmaceuticals.
1 comment:
Propolis has many indications in herbal medicine, but so far its properties have been little studied by scientists. They even have been prevented many times to do it, especially by the big pharmaceutical groups wish preservation of markets. Bee Propolis is a product very different from one area to another, propolis collected from different areas with different properties, depending on the plants from which bees collect it. Basically bees collect secretions with which plants defend themselves (basically collect healing substances for different plants). If scientists could study different types of propolis, would discover cures for many diseases and drug makers would suffer.
Post a Comment