Friday, October 25, 2019
Honey May Help Prevent Osteoporosis, Promote Bone Health
A Review of Potential Beneficial Effects of Honey on Bone Health
BUY Concentrated Propolis in Veggie Capsules
BUY 3-Piece (2 Fountain Pens, Rollerball) Gift Set
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Sep 19;2019:8543618
Bone remodelling is a complex and tightly regulated process. Disruption of bone remodelling skewing towards resorption will cause osteoporosis and increase the risk of fragility fracture. Honey is a natural product containing various bioactive ingredients with health benefits, especially polyphenols.
Therefore, honey may be a novel dietary supplement to prevent osteoporosis. This review aims to summarize the current evidence on the effects of honey on bone health. The evidence reported so far indicates a skeletal-beneficial effect of honey in animal models of osteoporosis. However, the number of studies on humans is limited.
Honey can protect the bone via its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, primarily through its polyphenol content that acts upon several signalling pathways, leading to bone anabolic and antiresorptive effects.
In conclusion, honey is a potential functional food for bone health, but the dose and the bioactive contents of honey need to be verified prior to its application in humans.
Labels:
Honey
Tuesday, October 22, 2019
Propolis Mouthwash More Effective Against Oral Bacteria Than Listerine
Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect of Propolis and its Application in Mouthwash Production
Front Dent. 2019 Jan-Feb;16(1):1-12
BUY Concentrated Propolis in Veggie Capsules
BUY 3-Piece (2 Fountain Pens, Rollerball) Gift Set
Objectives:
Our purpose was to determine the antibacterial properties of propolis and to evaluate its use as an antibacterial mouthwash with minimal complications.
Materials and Methods:
In this experimental laboratory study, an alcoholic propolis extract was prepared. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was calculated for four bacterial species including Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans), Lactobacillus acidophilus (L. acidophilus), and Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis) using agar dilution. According to the MIC, a propolis antibacterial mouthwash was produced and compared to water, chlorhexidine (CHX), and Listerine using laboratory rats for clinical examination. Salivary specimens of rats were collected at 12 hours, 1 week, and 2 weeks after using the mouthwash and examined by real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and repeated measures ANOVA (α = 0.05).
Results:
The results of agar dilution by the number of colony-forming units showed the lowest MIC for S. aureus and the highest for L. acidophilus. Our RT-PCR findings indicated that water alone had no effect on the level of oral bacteria. Propolis mouthwash showed a significant difference with CHX and Listerine (P < 0.05) in terms of the number of S. mutans, E. faecalis, and L. acidophilus colonies, while CHX and Listerine were less efficient. There was no significant difference between CHX and propolis (P = 0.110) regarding S. aureus colonies, but Listerine had a lower efficacy than either (P < 0.05).
Conclusion:
According to the results, propolis mouthwash was more efficient against the studied oral bacteria compared to CHX and Listerine.
Labels:
Propolis
Sunday, October 20, 2019
Propolis Boosts Healing of Diabetic Foot Wounds
Propolis as an Adjuvant in the Healing of Human Diabetic Foot Wounds Receiving Care in the Diagnostic and Treatment Centre from the Regional Hospital of Talca
J Diabetes Res. 2019 Sep 12;2019:2507578
UY Concentrated Propolis in Veggie Capsules
BUY 3-Piece (2 Fountain Pens, Rollerball) Gift Set
Objective:
Diabetic foot wounds are a relevant diabetes complication and a major health problem. It has been described that propolis has health benefits due to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and support in the healing process. The current study assessed the effect of propolis as an adjuvant in the healing of human diabetic foot ulcers. This was evaluated in a randomized placebo-controlled study of subjects receiving care in the Diagnostic and Treatment Centre from the Regional Hospital of Talca, Chile.
Research Design and Methods:
Randomized subjects received ambulatory healing treatment for diabetes foot wounds with propolis spray (3%), which was applied to cover the entire wound surface each time it was dressed from week 0 until cicatrization or 8 weeks as a maximum. Two serum samples were taken (day 0 and end of the study) for cytokine and oxidative stress analyses. Also, macro- and microscopy were analyzed in the process of wound healing.
Results:
The study comprised 31 subjects with type 2 diabetes in treatment for diabetic foot wounds in the Diagnostic and Treatment Centre from the Regional Hospital of Talca. Propolis promotes a reduction of the wound's area by an average of 4 cm2, related to an increase in the connective tissue deposit compared to the control. Also, propolis increased the glutathione (GSH) and GSH/glutathione disulfide (GSSG) ratio (p < 0.02), depleted tumor necrosis factor- (TNF-) α, and increased interleukin- (IL-) 10 levels. Topical propolis did not modify the biochemical parameters in the serum of the studied subjects.
Conclusions:
The topical use of propolis turned out to be an interesting therapeutic strategy as an adjuvant in the care of diabetes foot wounds due to its ability to improve and promote healing based on its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant profile.
Labels:
Propolis
Saturday, October 19, 2019
Bee Pollen Protects Nervous System
The therapeutic and protective effects of bee pollen against prenatal methylmercury induced neurotoxicity in rat pups
Metab Brain Dis. 2019 Oct 17
BUY Concentrated Propolis in Veggie Capsules
BUY 3-Piece (2 Fountain Pens, Rollerball) Gift Set
The current study evaluated the protective and therapeutic potency of bee pollen in ameliorating the toxic effects of methylmercury (MeHg), by measuring certain biochemical parameters related to neurotransmission, neuroinflammation, apoptosis, and glutamate excitotoxicity in the male neonate brain.
Healthy, pregnant female rats (N = 40) were randomly divided into 5 groups, each comprising10 male neonates, as follows: (i) neonates delivered by control mothers; (ii) neonates delivered by MeHg-treated mothers who received 0.5 mg/kg BW/day MeHg via drinking water from gestational day 7 till postnatal day 7; (iii) neonates delivered by bee pollen treated mothers who received 200-mg/kg BW bee pollen from postnatal day 0 for 4 weeks; (iv) protective group of neonates delivered by MeHg and bee pollen-treated mothers, who continued to receive bee pollen until day 21 at the same dose, and (v) therapeutic group of neonates delivered by MeHg- treated mothers followed by bee pollen treatment, wherein they received 200-mg/kg BW bee pollen from postnatal day 0 for 4 weeks.
Selected biochemical parameters in brain homogenates from each group were measured. MeHg-treated groups exhibited various signs of brain toxicity, such as a marked reduction in neurotransmitters (serotonin (5-HT), nor-adrenalin (NA), dopamine (DA)) and gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and elevated levels of interferon gamma (IFN-γ), caspase-3, and glutamate (Glu). Bee pollen effectively reduced the neurotoxic effects of MeHg. Minimal changes in all measured parameters were observed in MeHg-treated animals compared to the control group.
Therefore, bee pollen may safely improve neurotransmitter defects, inflammation, apoptosis, and glutamate excitotoxicity.
Metab Brain Dis. 2019 Oct 17
BUY Concentrated Propolis in Veggie Capsules
BUY 3-Piece (2 Fountain Pens, Rollerball) Gift Set
The current study evaluated the protective and therapeutic potency of bee pollen in ameliorating the toxic effects of methylmercury (MeHg), by measuring certain biochemical parameters related to neurotransmission, neuroinflammation, apoptosis, and glutamate excitotoxicity in the male neonate brain.
Healthy, pregnant female rats (N = 40) were randomly divided into 5 groups, each comprising10 male neonates, as follows: (i) neonates delivered by control mothers; (ii) neonates delivered by MeHg-treated mothers who received 0.5 mg/kg BW/day MeHg via drinking water from gestational day 7 till postnatal day 7; (iii) neonates delivered by bee pollen treated mothers who received 200-mg/kg BW bee pollen from postnatal day 0 for 4 weeks; (iv) protective group of neonates delivered by MeHg and bee pollen-treated mothers, who continued to receive bee pollen until day 21 at the same dose, and (v) therapeutic group of neonates delivered by MeHg- treated mothers followed by bee pollen treatment, wherein they received 200-mg/kg BW bee pollen from postnatal day 0 for 4 weeks.
Selected biochemical parameters in brain homogenates from each group were measured. MeHg-treated groups exhibited various signs of brain toxicity, such as a marked reduction in neurotransmitters (serotonin (5-HT), nor-adrenalin (NA), dopamine (DA)) and gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and elevated levels of interferon gamma (IFN-γ), caspase-3, and glutamate (Glu). Bee pollen effectively reduced the neurotoxic effects of MeHg. Minimal changes in all measured parameters were observed in MeHg-treated animals compared to the control group.
Therefore, bee pollen may safely improve neurotransmitter defects, inflammation, apoptosis, and glutamate excitotoxicity.
Labels:
Bee-Collected Pollen
Thursday, October 17, 2019
Iranian Propolis Inhibits Cancer Cell Growth
Iranian propolis efficiently inhibits growth of oral streptococci and cancer cell lines
BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine
BUY Concentrated Propolis in Veggie Capsules
BUY 3-Piece (2 Fountain Pens, Rollerball) Gift Set
Background
Propolis is a natural bee product with a wide range of biological activities that are related to its chemical composition. The present study investigated the quantification of quercetin (Q) in Ardabil ethanol extract of propolis (AEEP), and then compared its anti-bacterial, anti- biofilm and cytotoxic effects on cancer and normal cell lines.
Method
In the present study, the chemical composition of AEEP was determined through the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The AEEP and its main component, quercetin (Q), were evaluated in vitro against 57 oral streptococci by a broth micro-dilution method. The biofilm formation was assessed through the crystal violet staining and MTT assays. The impact of AEEP and Q anti-proliferative effect were evaluated on the fibroblast as normal and cancer cell lines (KB and A431).
Results
The Q concentration in the composition of AEEP was 6.9% of all its components. The findings indicated that the AEEP and Q were efficient against the cariogenic bacteria and were able to inhibit the S.mutans biofilm adherence at a sub-MIC concentration. Moreover, electron micrographs indicated the inhibition of biofilms compared to control biofilms. In addition, the AEEP and Q indicated a dose-dependent cytotoxic effect on A431 and KB cell lines. On the contrary, they had no cytotoxic effect on fibroblast cells.
Conclusion
The results indicated that the synergistic impact of main components of AEEP was related to the inhibition of the cancer cell proliferation, cariogenic bacteria and oral biofilm formation. It may play a promising role in the complementary medicine and, it is suggested to be used as food additives.
Labels:
Propolis
Wednesday, October 16, 2019
Propolis Helps Treat Diabetic Foot Wounds
Propolis as an Adjuvant in the Healing of Human Diabetic Foot Wounds Receiving Care in the Diagnostic and Treatment Centre from the Regional Hospital of Talca
J Diabetes Res. 2019 Sep 12;2019:2507578
BUY Concentrated Propolis in Veggie Capsules
BUY 3-Piece (2 Fountain Pens, Rollerball) Gift Set
Objective:
Diabetic foot wounds are a relevant diabetes complication and a major health problem. It has been described that propolis has health benefits due to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and support in the healing process. The current study assessed the effect of propolis as an adjuvant in the healing of human diabetic foot ulcers. This was evaluated in a randomized placebo-controlled study of subjects receiving care in the Diagnostic and Treatment Centre from the Regional Hospital of Talca, Chile.
Research Design and Methods:
Randomized subjects received ambulatory healing treatment for diabetes foot wounds with propolis spray (3%), which was applied to cover the entire wound surface each time it was dressed from week 0 until cicatrization or 8 weeks as a maximum. Two serum samples were taken (day 0 and end of the study) for cytokine and oxidative stress analyses. Also, macro- and microscopy were analyzed in the process of wound healing.
Results:
The study comprised 31 subjects with type 2 diabetes in treatment for diabetic foot wounds in the Diagnostic and Treatment Centre from the Regional Hospital of Talca. Propolis promotes a reduction of the wound's area by an average of 4 cm2, related to an increase in the connective tissue deposit compared to the control. Also, propolis increased the glutathione (GSH) and GSH/glutathione disulfide (GSSG) ratio (p < 0.02), depleted tumor necrosis factor- (TNF-) α, and increased interleukin- (IL-) 10 levels. Topical propolis did not modify the biochemical parameters in the serum of the studied subjects.
Conclusions:
The topical use of propolis turned out to be an interesting therapeutic strategy as an adjuvant in the care of diabetes foot wounds due to its ability to improve and promote healing based on its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant profile.
Labels:
Propolis
Tuesday, October 15, 2019
Combined Protective Effects of Malaysian Propolis and Metformin Improve Diabetic Male Fertility
Oxidative Stress, NF-κB-Mediated Inflammation and Apoptosis in the Testes of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats: Combined Protective Effects of Malaysian Propolis and Metformin
Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Oct 9;8(10). pii: E465
BUY Concentrated Propolis in Veggie Capsules
BUY 3-Piece (2 Fountain Pens, Rollerball) Gift Set
Oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis are major complications that trigger organ failure in diabetes mellitus (DM), and are proven to adversely affect the male reproductive system.
Clinical and experimental studies have demonstrated the promising protective effects of propolis in DM and its associated systemic effects. Herein, we investigated the effect of Malaysian propolis (MP) on testicular oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in diabetic rats. Further, the possibility of a complementary effect of MP with the anti-hyperglycaemic agent, metformin (Met), was studied with the idea of recommending its use in the event that Met alone is unable to contain the negative effects of DM on the male reproductive system in mind. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were either gavaged distilled water (normoglycaemic control and diabetic control groups), MP (diabetic rats on MP), Met (diabetic rats on Met) or MP+Met (diabetic rats on MP+Met), for 4 weeks. MP decreased oxidative stress by up-regulating (p < 0.05) testicular mRNA levels of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase; increasing (p < 0.05) the activities of antioxidant enzymes; and decreasing (p < 0.05) lipid peroxidation in the testes and epididymis of diabetic rats.
Further, MP down-regulated (p < 0.05) testicular mRNA and protein levels of pro-inflammatory mediators (nuclear factor kappa B, inducible nitric oxide synthase, tumour necrosis factor-α and interleukin (IL)-1β), decreased (p < 0.05) the nitric oxide level, and increased (p < 0.05) IL-10 mRNA and protein levels. MP also down-regulated (p < 0.05) Bax/Bcl-2, p53, casapase-8, caspase-9 and caspase-3 genes, and increased (p < 0.05) testicular germ cell proliferation. MP's effects were comparable to Met. However, the best results were achieved following co-administration of MP and Met.
Therefore, we concluded that administration of the MP+Met combination better attenuates testicular oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in DM, relative to MP or Met monotherapy, and may improve the fertility of males with DM.
Labels:
Propolis
Monday, October 14, 2019
Gelam Honey Promotes Corneal Wound Healing
Gelam honey promotes ex vivo corneal fibroblasts wound healing
Cytotechnology. 2019 Oct 12
BUY Concentrated Propolis in Veggie Capsules
BUY 3-Piece (2 Fountain Pens, Rollerball) Gift Set
This study evaluated the effects of Gelam honey (GH) on ex vivo corneal fibroblast ulcer model via wound healing assay, gene expression and immunocytochemistry.
Corneal fibroblasts from New Zealand white rabbits were culture expanded. The corneal fibroblast wound healing capacity was observed by creating a circular wound onto confluent monolayer cells cultured in basal medium (BM), BM with GH, serum-enriched basal medium (BMS) and BMS with GH respectively.
Wound healing assay and phenotypic characterization of the corneal fibroblast were performed at different stages of wound closure. Expression of aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), vimentin, α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), lumican, collagen I and matrix metalloproteinase 12 (MMP 12) were measured at day 1, day 3 and complete wound closure day. Corneal fibroblast cultured in BMS with GH demonstrated the fastest wound closure, at day 5 post wounding.
The gene expressions of ALDH and vimentin were higher than control groups while α-SMA expression was lower, in GH enriched media. The expressions of lumican, collagen I and MMP 12 were also higher in cells cultured in GH enriched media compared to the control groups.
GH was shown to promote in vitro corneal fibroblast wound healing and may be a potential natural adjunct in the treatment of corneal wound.
Wednesday, October 09, 2019
Bee Venom Component May Help Restore Memory in Alzheimer’s Disease (Aging, Ageing, Dementia, Brain, Mental, Cognitive)
Bee venom phospholipase A2 ameliorates amyloidogenesis and neuroinflammation through inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 pathway in Tg2576 mice
Transl Neurodegener. 2019 Oct 2;8:26
BUY Concentrated Propolis in Veggie Capsules
BUY 3-Piece (2 Fountain Pens, Rollerball) Gift Set
Background:
Neuroinflammation and accumulation of β-amyloid (Aβ) play a significant role in the onset and progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Our previous study demonstrated that signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) plays a major role in neuroinflammation and amyloidogenesis.
Methods:
In the present study, we investigated the inhibitory effect of bee venom phospholipase A2 (bvPLA2) on memory deficiency in Tg2576 mice, which demonstrate genetic characteristics of AD and the mechanism of its action at the cellular and animal level. For in vivo study, we examined the effect of bvPLA2 on improving memory by conducting several behavioral tests with the administration of bvPLA2 (1 mg/kg) to Tg2576 mice. For in vitro study, we examined the effect of bvPLA2 on amyloidogenesis and neuroinflammation by treating bvPLA2 on LPS-activated BV2 cells.
Results:
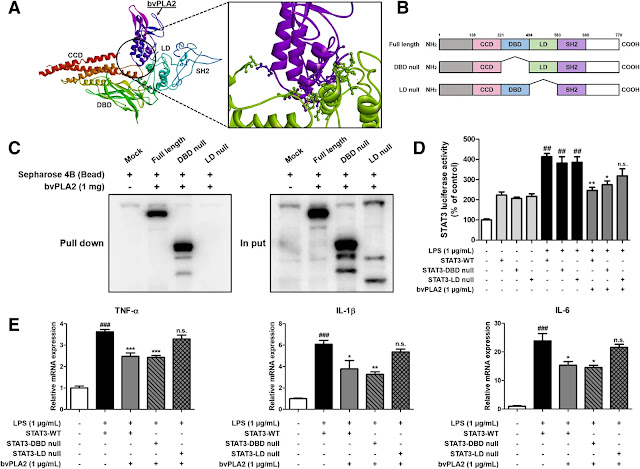
We found that bvPLA2 alleviated memory impairment in Tg2576 mice, as demonstrated in the behavioral tests assessing memory. In the bvPLA2-treated group, Aβ, amyloid precursor protein (APP), and β-secretase 1 (BACE1) levels and β-secretase activity were significantly decreased. Expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inflammation-related proteins decreased in the brain of bvPLA2-treated group, whereas anti-inflammatory cytokines increased. In addition, bvPLA2 reduced STAT3 phosphorylation in the brains of the bvPLA2-treated group. At the cellular level, bvPLA2 inhibits production of nitric oxide, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and inflammation-related proteins including p-STAT3. Additionally, bvPLA2 inhibits the production of Aβ in cultured BV-2 cells. Results from the docking experiment, pull-down assay, and the luciferase assay show that bvPLA2 directly binds STAT3 and, thus, regulates gene expression levels. Moreover, when the STAT3 inhibitor and bvPLA2 were administered together, the anti-amyloidogenic and anti-inflammatory effects were further enhanced than when they were administered alone.
Conclusion:
These results suggest that bvPLA2 could restore memory by inhibiting the accumulation of Aβ and inflammatory responses via blockage of STAT3 activity.
Labels:
Bee Venom
Tuesday, October 08, 2019
Propolis Prevents Damage to the Liver
Protective Role of Propolis on Low and High Dose Furan-induced Hepatotoxicity and Oxidative Stress in Rats
J Vet Res. 2019 Sep 13;63(3):423-431
BUY Concentrated Propolis in Veggie Capsules
BUY 3-Piece (2 Fountain Pens, Rollerball) Gift Set
Introduction:
The aim of this study was to evaluate potential protective effects of propolis on furan-induced hepatic damage by assessing the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and reduced glutathione (GSH), antioxidant enzyme activities, and histopathological changes in the liver.
Material and Methods:
Albino Wistar rats were divided into six groups: a control, propolis-treated (100 mg/kg b.w./day), low-dose furan-treated (furan-L group; 2 mg/kg b.w./day), high-dose furan-treated (furan-H group; 16 mg/kg b.w./day), furan-L+propolis treated, and furan-H+propolis treated group. Propolis and furan were applied by gavage; propolis for 8 days, and furan for 20 days in furan-L groups and 10 days in furan-H groups.
Results:
While MDA levels were elevated in furan-treated groups, levels of GSH and activities of antioxidant enzymes decreased (p < 0.001). The levels of MDA and GSH and activities of antioxidant enzymes were normal in the furan+propolis groups, especially in the furan-L+propolis group (p < 0.001). While the aspartate transaminase, alanine transaminase, alkaline phosphatase, and lactate pdehydrogenase activities were elevated in the furan-H treated group (p < 0.05 and p < 0.001), they were unchanged in the furan-L treated group. Histopathologically, several lesions were observed in the liver tissues of the furan-treated groups, especially in the higher-dose group. It was determined that these changes were milder in both of the furan+propolis groups.
Conclusion:
The results indicate that propolis exhibits good hepatoprotective and antioxidant potential against furan-induced hepatocellular damage in rats.
Labels:
Propolis
Monday, October 07, 2019
MGO™ Manuka Honey Inhibits Infectious Diseases
Oligosaccharides Isolated from MGO™ Manuka Honey Inhibit the Adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia Coli O157:H7 and Staphylococcus Aureus to Human HT-29 cells
Foods. 2019 Oct 1;8(10). pii: E446
BUY Concentrated Propolis in Veggie Capsules
BUY 3-Piece (2 Fountain Pens, Rollerball) Gift Set
Historically, honey is known for its anti-bacterial and anti-fungal activities and its use for treatment of wound infections.
Although this practice has been in place for millennia, little information exists regarding which manuka honey components contribute to the protective nature of this product. Given that sugar accounts for over 80% of honey and up to 25% of this sugar is composed of oligosaccharides, we have investigated the anti-infective activity of manuka honey oligosaccharides against a range of pathogens.
Initially, oligosaccharides were extracted from a commercially-available New Zealand manuka honey-MGO™ Manuka Honey (Manuka Health New Zealand Ltd)-and characterized by High pH anion exchange chromatography coupled with pulsed amperiometric detection. The adhesion of specific pathogens to the human colonic adenocarcinoma cell line, HT-29, was then assessed in the presence and absence of these oligosaccharides. Manuka honey oligosaccharides significantly reduced the adhesion of Escherichia coli O157:H7 (by 40%), Staphylococcus aureus (by 30%), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (by 52%) to HT-29 cells. This activity was then proven to be concentration dependent and independent of bacterial killing.
This study identifies MGO™ Manuka Honey as a source of anti-infective oligosaccharides for applications in functional foods aimed at lowering the incidence of infectious diseases.
Foods. 2019 Oct 1;8(10). pii: E446
BUY Concentrated Propolis in Veggie Capsules
BUY 3-Piece (2 Fountain Pens, Rollerball) Gift Set
Historically, honey is known for its anti-bacterial and anti-fungal activities and its use for treatment of wound infections.
Although this practice has been in place for millennia, little information exists regarding which manuka honey components contribute to the protective nature of this product. Given that sugar accounts for over 80% of honey and up to 25% of this sugar is composed of oligosaccharides, we have investigated the anti-infective activity of manuka honey oligosaccharides against a range of pathogens.
Initially, oligosaccharides were extracted from a commercially-available New Zealand manuka honey-MGO™ Manuka Honey (Manuka Health New Zealand Ltd)-and characterized by High pH anion exchange chromatography coupled with pulsed amperiometric detection. The adhesion of specific pathogens to the human colonic adenocarcinoma cell line, HT-29, was then assessed in the presence and absence of these oligosaccharides. Manuka honey oligosaccharides significantly reduced the adhesion of Escherichia coli O157:H7 (by 40%), Staphylococcus aureus (by 30%), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (by 52%) to HT-29 cells. This activity was then proven to be concentration dependent and independent of bacterial killing.
This study identifies MGO™ Manuka Honey as a source of anti-infective oligosaccharides for applications in functional foods aimed at lowering the incidence of infectious diseases.
Labels:
Honey
Saturday, October 05, 2019
Swiss Honeydew Honey Shows Higher Antibacterial Activity
Antibacterial potential of Swiss honeys and characterisation of their bee-derived bioactive compounds
J Sci Food Agric. 2019 Oct 4
BUY Concentrated Propolis in Veggie Capsules
BUY 3-Piece (2 Fountain Pens, Rollerball) Gift Set
BACKGROUND:
Antibacterial activity of honey is not only crucial characteristic in selection of honey for medical usage but also an important honey quality marker. The aim of the study was to characterize the antibacterial potential of 29 honey samples representing the main types of multi-floral blossom and honeydew honeys produced in Switzerland. Antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa was expressed as a minimum inhibitory and bactericidal concentrations (MIC and MBC). Furthermore, the content of bee derived glucose oxidase (GOX) and its enzymatic product, H2 O2 , were also evaluated.
RESULTS:
All honey samples successfully met basic defined criteria (moisture and hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF)) tested in this study. Honeydew honeys were the most effective honey samples and generated the highest levels of H2 O2 . A strong significant correlation was found between the overall antibacterial activity and the level of H2 O2 among all honey samples. Interestingly, the content of GOX in honey samples did not correlate with their antibacterial activity as well as H2 O2 production capacity. A weak antibacterial activity was determined in 5 floral honeys, most likely due to increased enzymatic activity of pollen-derived catalase.
CONCLUSION:
This study showed that antibacterial effect of Swiss honey samples is associated mainly with H2 O2 .
Labels:
Honey
Friday, October 04, 2019
Brazilian Propolis Protects Against Risk Factor for Aging (Anti-Aging)
The Protective Effect of Brazilian Propolis against Glycation Stress in Mouse Skeletal Muscle
Foods. 2019 Sep 25;8(10). pii: E439
BUY Concentrated Propolis in Veggie Capsules
BUY 3-Piece (2 Fountain Pens, Rollerball) Gift Set
We investigated the protective effect of Brazilian propolis, a natural resinous substance produced by honeybees, against glycation stress in mouse skeletal muscles. Mice were divided into four groups: (1) Normal diet + drinking water, (2) Brazilian propolis (0.1%)-containing diet + drinking water, (3) normal diet + methylglyoxal (MGO) (0.1%)-containing drinking water, and (4) Brazilian propolis (0.1%)-containing diet + MGO (0.1%)-containing drinking water. MGO treatment for 20 weeks reduced the weight of the extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscle and tended to be in the soleus muscle.
Ingestion of Brazilian propolis showed no effect on this change in EDL muscles but tended to increase the weight of the soleus muscles regardless of MGO treatment. In EDL muscles, Brazilian propolis ingestion suppressed the accumulation of MGO-derived advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in MGO-treated mice. The activity of glyoxalase 1 was not affected by MGO, but was enhanced by Brazilian propolis in EDL muscles. MGO treatment increased mRNA expression of inflammation-related molecules, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Brazilian propolis ingestion suppressed these increases. MGO and/or propolis exerted no effect on the accumulation of AGEs, glyoxalase 1 activity, and inflammatory responses in soleus muscles.
These results suggest that Brazilian propolis exerts a protective effect against by inhibiting the accumulation of AGEs, promoting MGO detoxification, and reducing proinflammatory responses in the skeletal muscle. However, these anti-glycation effects does not lead to prevent glycation-induced muscle mass reduction.
Labels:
Propolis
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)